About Us
HISTORY OF HEALTHCARE COALITIONS
2001 - The origination of healthcare coalitions, and the associated Hospital Preparedness Program (HPP), can be traced back to the events of September 11, 2001 and the subsequent anthrax attacks later that same year. These events highlighted the lack of preparedness for bioterrorist attacks in the U.S.
2002 - In 2002, in an effort to address these gaps at the hospital level, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR) created the Hospital Preparedness Program (HPP). This new Federal program provided funding to states to build capacity around activities associated with decontamination, pharmaceutical caches, hospital bed surge capacity, and training.
2004 - In 2004, the emphasis of the HPP program shifted to an all-hazards approach and put a greater emphasis on hospitals, as well as other healthcare systems (urgent cares, private practices, long-term care facilities, behavioral health centers, etc.), to demonstrate their ability to perform functions associated with all types of responses. It was this shift that gave rise to Healthcare Coalitions, which are now mandated and required by the Federal government to exist in all states and regions of the U.S.
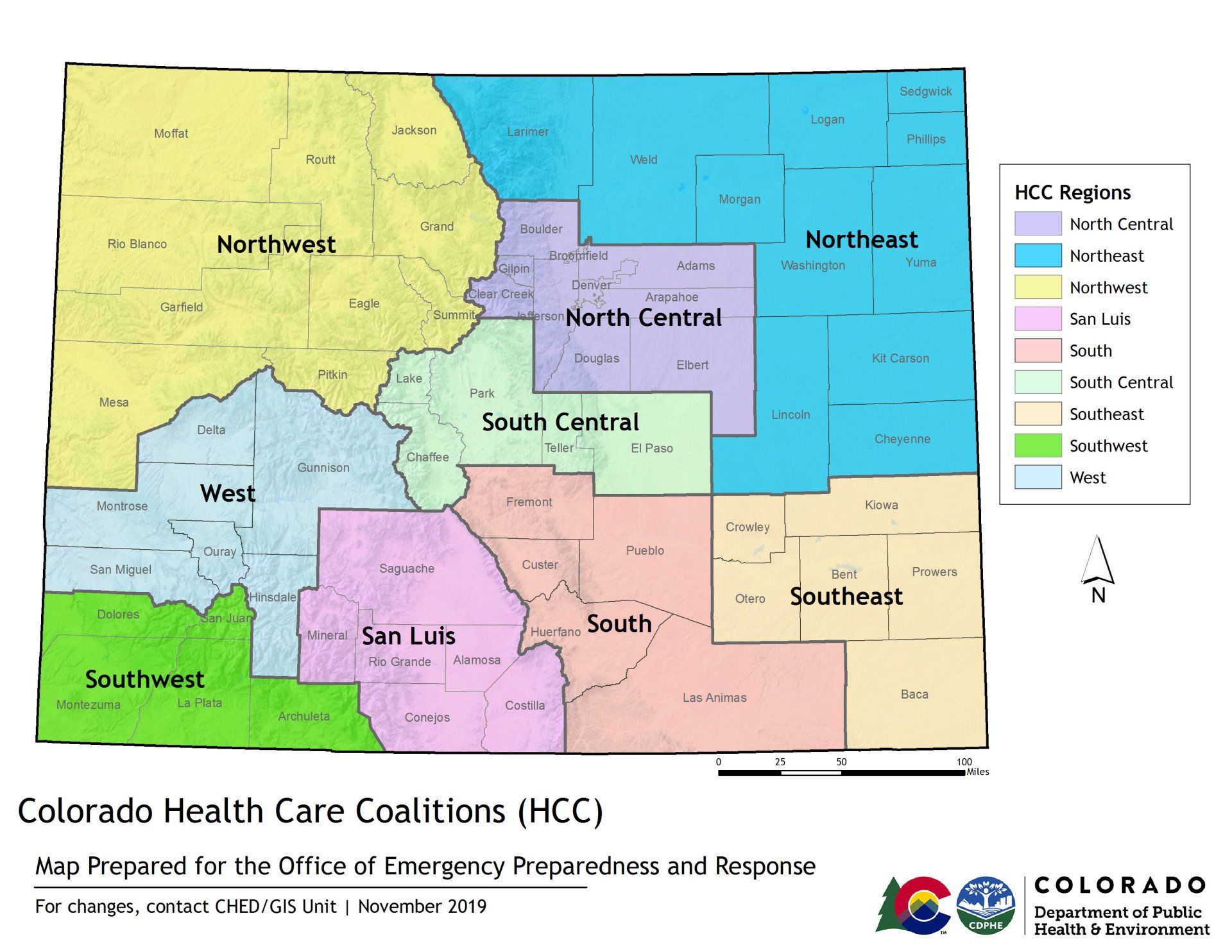
2017 - Healthcare coalitions in the State of Colorado have been in existence since the inception of the HPP, however, in 2017 federal and local initiatives shifted the focus of preparedness efforts to regional levels. Under this new structure, the number of healthcare coalitions was consolidated from just over 30 to nine. The new boundaries for Colorado’s nine coalitions were developed to better align Healthcare Coalition Regions with All-Hazards Emergency Management Regions. This geographical tactic is an effort to better support regional initiatives and the development of a Regional Healthcare Disaster Response System (RHDRS).
2020 - Today, healthcare coalitions continue to function with an all-hazards approach. Over the years, the primary activities and membership has grown and evolved to include non-healthcare related agencies (such as public health departments, emergency management, and schools) but the core mission has remained the same: to prepare the healthcare delivery system to continue providing healthcare services and save lives during emergencies and disaster events that exceed the day-to-day capacity and capability of existing health and emergency response systems.
How do Healthcare Coalitions Work?
Through Regional Preparedness Activities
- Identify collective threats, risks, and vulnerabilities.
- Assess resources and capabilities.
- Identify gaps in resources and capabilities.
- Develop plans for shared responses.
- Identify pathways of communication and situational awareness
Through Regional Response Activities
- Share Elements of Essential Information and Critical Information Requirements in order to develop situational awareness and a common operating picture.
- Support Local and State "Emergency Support Function 8 – Health and Medical Coordination".
- Support Resource Needs by identifying critical infrastructure, personnel, and supplies during times of community or member organization crisis.
- Participate in response missions to assure the delivery of critical healthcare services to people in need.